BSCI 230 Today, 2/15/01
Lecture 6 - Glycolysis - TCA
Review procedures for posting to eCell
Any problems or concerns?
Introduction of recitation TAs
Demotivational thought for the day
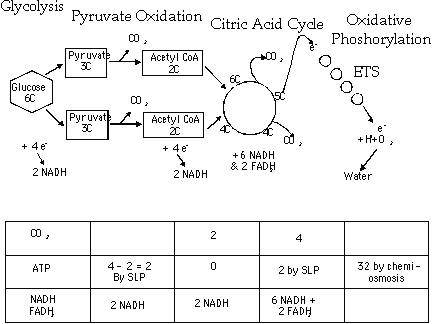
Glycolysis, oxidation of pyruvate, Krebs TCA Cycle, and oxidative
phosphorylation
Your Recitation Leaders:
Carsten
Darren
Diane
Lauren
Lisa
Mario
Michael
Payman
Usman
Oops!
C6H12O6 + 6O2 <---> 6CO2 + 6 H2O
DG = - 686 kcal/mole
Oxidation of (CH2O)6
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
Chemiosmotic Synthesis
NAD+ and FAD
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
(SLP)
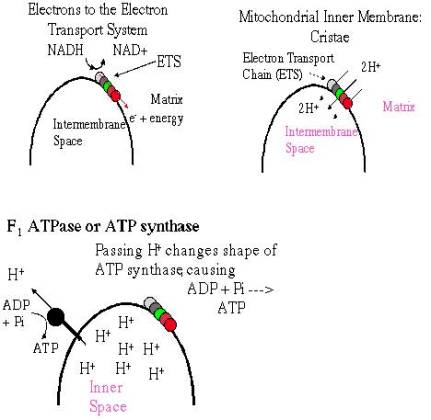
Summary of Chemiosmotic Synthesis of ATP
1. High energy e- carried by NADH and FADH2
2. To mitochondrial ETS on cristae
3. e- loses energy on ETS which uses it to pump H+ into
intermembrane space
4. [H+] gradient used to allow H+ diffuse through ATP
synthase and make ATP
Electrons to the Electron Transport System
Mitochondrial Inner Membrane: Cristae
To Our Handout:
What to know for each process!!!
What you start with
What you end with
Where it occurs?
Whatís the point?
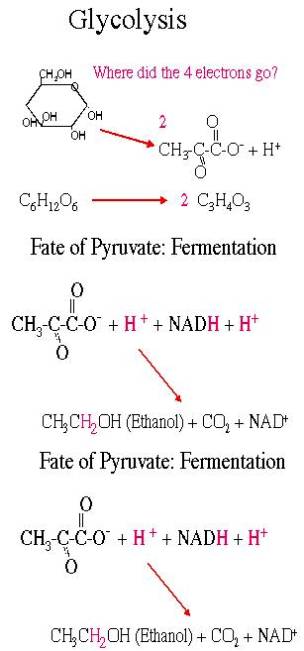
Glycolysis
Glucose (6C) +2 NAD+ + 2 ATP --->
2 Pyruvate (3C) + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 4 ATP
Glycolysis
Cytoplasmic
Uses 2 ATP to generate 4 ATP
Net gain of 2 ATP
Generates ATP anaerobically by SLP
- Relatively low yield of energy
Generates 2 NADH
Fate of Pyruvate in the absence of oxygen:
Fermentation
Fig 13-9
Purpose: regenerate NAD+ to allow anaerobic glycolysis
and SLP to occur
Fate of Muscle Lactate
(Running is bad for you)
Anaerobic conditions: muscles can make ATP by SLP but lactate
builds up
Recovery phase involves gluconeogenesis in the liver
Cori Cycle
Endergonic, reduction reaction
Regulation of Glycolysis by Allosteric Mechanisms
Activation by ADP and AMP
Inhibition by Acetyl CoA and ATP
See Fig 13-13 to be sure you understand the theory behind
these allosteric actions
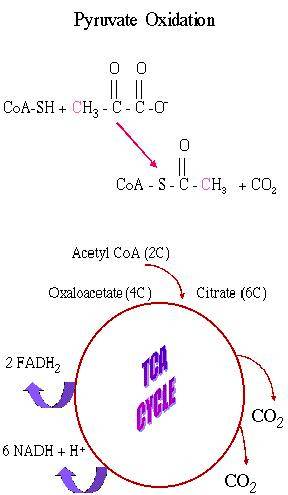
Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate + Coenzyme A* + NAD+ --->
Acetyl CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+
*written as CoA-SH
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
Step 1:
Acetyl CoA (2C) + Oxaloacetate (4C) ---> Citrate (6C)
+ CoA-SH