
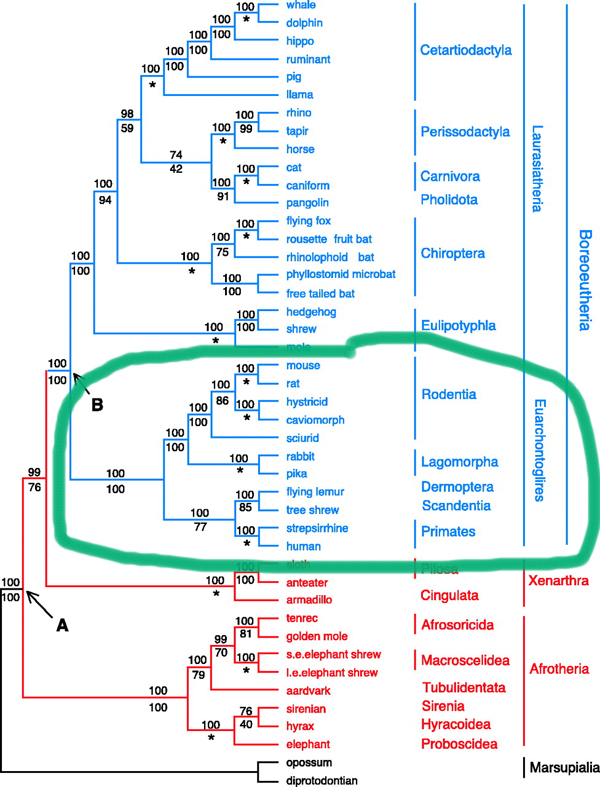
The superorder Euarchontaglires is comprised of five orders:
- Rodentia
- Lagomorpha
- Dermoptera
- Scandentia
- Primates
| Common names |
mice, rats, porcupines, etc. |
| # of Families |
37 |
| # of Species |
~2300 |
| Distribution |
Worldwide |
- Convergence with other eutherian mammals
- Most notable characteristic: Teeth
- Rootless
- Incisors
- Cheek teeth
- Diastema
- Complex muscles to control chewing and gnawing
- Major groups (originally based on jaw musculature and morphology)
- Protrognaths: ancestral condition (ex. Aplodontidae)
- Sciuromorphs: squirrel-like
- Myomorphs: rats, mice
- Hystricomorphs: guinea pig and porcupine
- Selected families
- Aplodontidae (mountain beaver)
- Sciuridae (tree squirrels, ground squirrels, flying squirrels)
- Castoridae (beaver)
- Heteromyidae (kangaroo rats)
- Muridae (rats and mice)
- Hystricidae (Old World porcupines)
- Erethizontidae (New World porcupines)
- Cavidae (guinea pigs, mara)
| Common names |
rabbits, hares and pikas |
| # of Species |
~80 |
| Distribution |
Nearly worldwide |
- Characteristics related to diet
- Teeth
- Incisors
- No canines
- Cheek teeth - lower jaw narrower than upper jaw
- Characteristics related to mode of locomotion (quadrupedal saltatory)
- Digitigrade/ plantigrade
- Skull
- Fenestration
- Jointed
- Soles of feet are furred
- Tail is short or absent
- Families
- Ochotonidae (pikas)
- Leporidae (desert cottontail rabbit, antelope jackrabbit)
Lagomorph? Artiodactyl?
Name means "skin wing"
Common name (flying lemur) is a misnomer...
Two species (Distribution: Philipines; Malaysia)
- Taxonomy (phylogenetic relationship to bats and primates)
- "Volitantia hypothesis" - bats and flying lemurs are sister taxa
- "Primatomorpha hypothesis" - primates and flying lemurs are sister taxa
- "Mammalia incertae sedis" - who knows...
- Morphology
- Patagium most complete of any mammal
- Pectinate incisors
- Ecology and behavior
- Nocturnal or crepuscular
- Folivorous (see skull), have greatly enlarged cecum
- Solitary (?) and territorial (?)
- Best gliders of all mammals
| Common name |
Tree shrews |
| Families |
1 (Tupaiidae) |
| # of genera |
5 |
| # of species |
19 |
| Distribution |
S.E. Asia (tropical) |
- Characteristics of the order
- Once considered a primitive primate, then lumped with Insectivora
- Important differences between tree shrews and insectivores:
- Complete zygomatic arch
- Has auditory bullae
- Big brain case for its size
- Has a cecum
- Look like squirrels (long furry tails)
- Big eyes
- Teeth resemble insectivores somewhat (caniform incisor, reduced canine)
- Ecology and behavior
- Arboreal
- Diurnal (for the most part)
- Omnivorous (eats fruits, seeds, some insects)
- Some are social, some appear to live in pairs
- Reproduction
- Young left in a separate nest
- Nursed once/48 h
- Weaned in a month
V. Order Primates
2 suborders, 13 families, 232 species
Worldwide distribution
- General characteristics (adaptations for arboreality?)
- Locomotion
- Pentadactyly
- Nails in stead of claws (unguiculate)
- Prehensility of hands and feet
- Traction ridges on tips of digits
- Tendency towards erectness of posture
- Teeth and diet
- Generalized teeth (bunodont molars)
- Generalized diet
- Brain and behavior
- More reliance on vision (forward facing eyes, binocular, stereoscopic, most have color vision)
- Reduction of snout
- Big, complex brains (especially cerebral cortex)
- Flexibility of behavior
- In many species, complex social organization
- Reproduction
- Long gestation
- Single births common
- Slow development
- Long lifespan
- Living primates
- Suborder Strepsirhini
- General characteristics
- ancestral morphology and possibly behavior
- restricted geographical range (Old World)
- rhinarium
- toothcomb and toilet claw
- tapetum lucidum
- bicornuate uterus
- Families
- Family Lemuridae (lemurs) - Madagascar
- Family Cheirogaleidae (dwarf and mouse lemurs) - Madagascar
- Family Megaladapidae (sportive lemurs) - Madagascar
- Family Indridae (indri, sifaka) - Madagascar
- striking coloration pattern
- long snout
- short tail
- elongated hind limbs
- vertical clingers and leapers
- VIDEO
- Family Daubentoniidae (aye-aye) - Madagascar
- Family Loridae (lorises) - Africa, S.E. Asia
- Family Galagonidae (galagos) - Africa
- Suborder Haplorhini
- General characteristics
- lack rhinarium
- spatulate incisors
- simplex uterus
- Families
tarsiers, platyrrhini (New World) and catarrhini (Old World)
- Family Tarsiidae (tarsiers) - S.E. Asia
- Family Callitrichidae (marmosets, tamarins) - Central and South America
- Family Cebidae (New World monkeys) - Central and South America
- Family Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys) - Africa, Asia
- Family Hylobatidae (gibbons) - Asia
- Family Hominidae (great apes, humans) - worldwide
LINK to Wisconsin Primate Research Center primate vocalizations library
LINK to Duke Lemur Center
LINK to Primates.com picture gallery


