

Why is body temperature (T) important? Relationship between metabolic enzymes and temperature
Tactics used to retain heat
|
Tactics used to dissipate heat or minimize heat gain
|

| Homeothermy worksheet #1 |
| Think-Pair-Share Why might they periodically warm up during hibernation? |
Skeletal structure

|
| Homeothermy worksheet #2 |
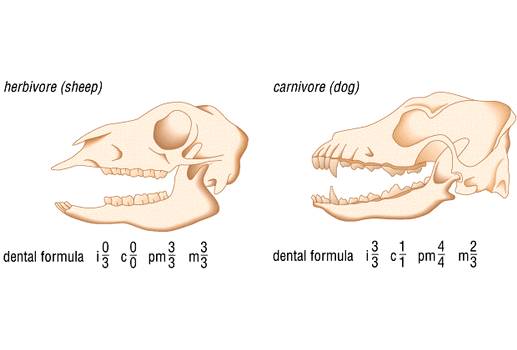
| Mode of foraging | Teeth | Tongue | Stomach | Intestines | Cecum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insectivory | numerous, spiky, incisors procumbent Example: mole Example: shrew | -- | simple | short | mostly lacking |
| Myrmecophagy | absent or reduced in numbers, peg-like Example: tamandua anteater | extremely long | simple, often roughened | short | small or lacking |
| Terrestrial carnivory | sharp incisors; long, conical canines; often carnassial cheek teeth; may have crushing molars Example: dog | -- | simple | short | small |
| Aquatic carnivory | homodont, spiky, numerous Example: common dolphin | -- | simple or multichambered (cetaceans only) | variable | small or absent |
| Sanguinivory | very sharp upper incisors; reduced cheek teeth Example: vampire bat | grooved | tubular, highly extensible | long | small or lacking |
| Herbivory (except nectivores) | incisors robust or absent; canines reduced or absent; diastema; cheek teeth enlarged with complex occlusal surfaces Example: beaver | -- | simple (hindgut fermenters) or multichambered (ruminants) | long | large |
| Filter feeding | none (baleen)
Example: blue whale | -- | multichambered | -- | present (for digesting chitin) |
| Omnivory | sharp incisors and canines; flat cheek teeth with rounded cusps
Example: bear | -- | simple | long | small |
