Lab 2. Cells of the Immune System
Peripheral Blood SmearProcedure:
1. Clean a microscope slide with 70% ethanol and lens paper.
2. Spray your left "ring " finger with 70% ethanol or wipe it with an alcohol wiper and let it air dry.
3. Take a sterile lancet and puncture your fingertip. If you have calluses, aim a little to the side. DO NOT LANCET ANYONE OTHER THAN YOURSELF. When finished with your lances, place them in the BIOHAZARD CONTAINER.
4. Place a small drop of blood on the end of the slide. At this point, put on GLOVES. DO NOT TOUCH ANYONE ELSE’S BLOOD.
5. Now you need to spread the blood out so that a single layer of cells is obtained. To do this, take a new “spreader” slide and place it in the center of you “blood” slide. Move it toward the drop of blood. When it contacts the drop, the blood will spread out along the edge of the “spreader” slide. Now comes the hard part. With a smooth motion, push the “spreader” slide back about 3/4 of the way toward the other side of the “blood” slide. This will pull the blood along with it.
6. Let the smear dry thoroughly.
7. Stain the smear with Wright stain as described on the accompanying sheet.
8. Let the smear dry thoroughly.
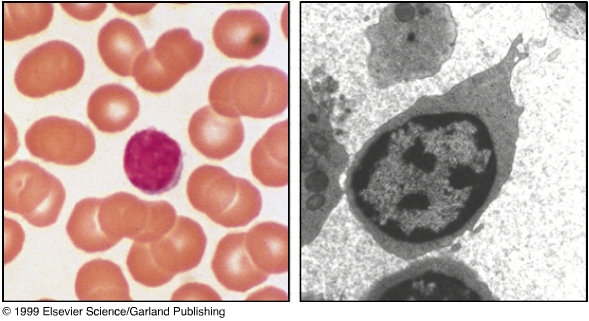
9. Examine the smear. Most of what you will see are red blood cells, but don’t count these. Count as many white blood cells as you can categorize as indicated on the figures below, with about 100 giving a good differential count. Record the number and percent of :
Cell Type Cell Number % Neutrophils Lymphocytes Monocytes Eosinophils Basophils Total 100 10. Dispose of slides in the BIOHAZARD waste.
Smear of human peripheral blood stained with Wright's stain.Human Peripheral Blood Cells
Cell Type Cells/ml blood (%) Function Erythrocytes 6,000,000 Oxygen transport Platelets 300,000 Blood clotting and blood vessel repair Neutrophils 5,000 (50-70%) Phagocytosis Lymphocytes 3,000 (20-30%) Specific immunity Monocytes 500 (2-6%) Phagocytosis and present antigens Eosinophiles 300 (1-5%) Destroy antibody-antigen complexes Basophils 30 (<1%) Unknown
Lymphocytes function in specific immunity