Concepts from Chapter 7
Action potential & graded potential
Mechanisms and details of synaptic transmission
Synaptic delay
Excitatory and Inhibitory synapses
IPSP and EPSP
Ionotropic and Metabotropic receptors
Temporal and Spatial summation
The neurotransmitters, pages 214 - 219
Agonist
Mimics action of NT
Antagonist (Blocker)
Binds to receptor and prevents NT action
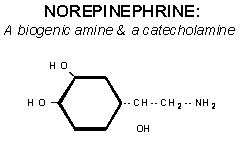
Biogenic amines
Catecholamines:
• Norepinephrine (noradrenalin)
• Epinephrine (adrenalin)
• Dopamine
Serotonin
Histamine

ADRENERGIC RECEPTORS
• ![]() - Excitatory
- Excitatory
• ![]() - Inhibitory
- Inhibitory
• ![]() - Excitatory
- Excitatory
• ![]() - Inhibitory
- Inhibitory
• ![]() - Excitatory
- Excitatory

CHOLINERGIC RECEPTORS
• NICOTINIC
• MUSCARINIC
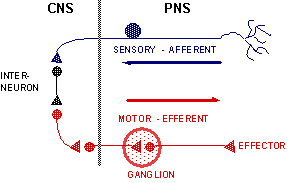
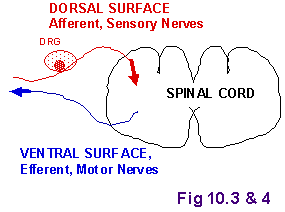
Nervous System
CNS
• Brain & Spinal Column
PNS
• Afferent - Sensory
• Efferent - Motor
Efferent Nervous System
(see image on Web and Fig 6.1)
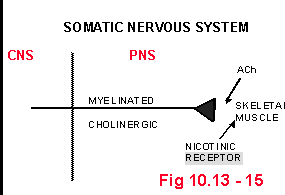
• Somatic
• Autonomic
• Parasympathetic
• Sympathetic
Table 10.1
SOMATIC vs. AUTONOMIC
• STRUCTURES INNERVATED
• MODE OF ACTION
• EFFECT OF DENERVATION
See Table 10.4
Fig 10.6: Parasympathetic Pathways
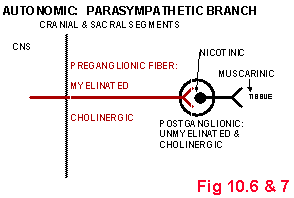
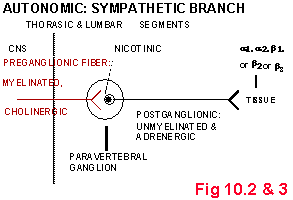
SYMPATHETIC vs. PARASYMPATHETIC
• OUTFLOWS FROM SPINAL CORD
• NEUROTRANSMITTERS
• DEGREE OF BRANCHING
• Preganglionic to Postganglionic
Ratio
• ACTIONS ON EFFECTORS
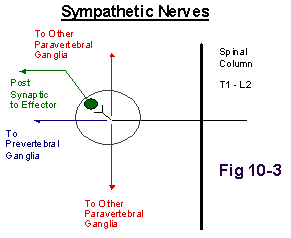
SYMPATHETIC ACTIONS
HEART RATE = +
HEART BEAT STRENGTH = +
BLOOD FLOW TO SKELETAL MUSCLE = +
BRONCHIOLE DIAMETER = +
BLOOD FLOW TO INTESTINE = -
BLOOD GLUCOSE = +
INTESTINAL ACTIVITY = -
PUPIL DIAMETER = +
SWEAT GLANDS = +
SYMPATHETIC RECEPTOR EXCEPTIONS
Sweat glands: ACh onto muscarinic (Excite)
Some blood vessels to skeletal muscles: ACh onto muscarinic (Inhibitory)
Adrenal Medulla
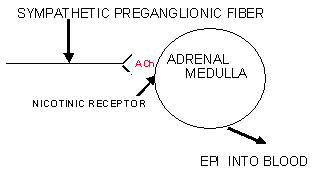
BLOOD VESSELS RECEIVE ONLY SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION!
PARASYMPATHETIC ACTIONS
IMAGINE: sleeping in a chair after a good meal!
You should now be able to understand and recreate Table 10.3
Presynaptic Inhibition
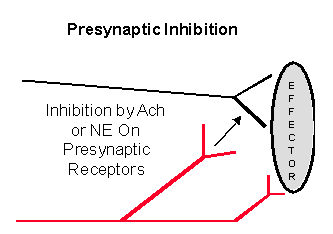
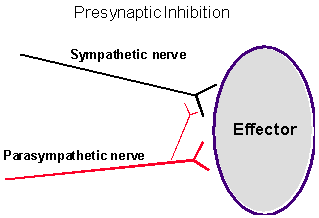
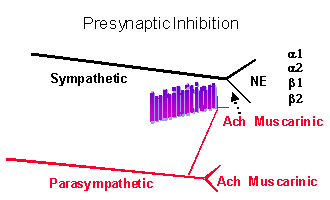
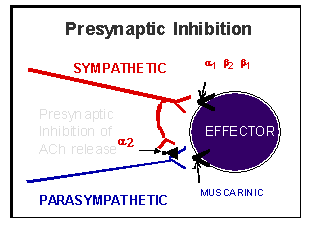
Make sure that you understand the ANS Pharmacology
Summary Table posted on the course Web site!!!!!!