ANS PHARMACOLOGY
Selected sections of Chapters 6, 7, &
10 of the Text
We will review drugs acting
at:
Axonal membrane
Cholinergic transmission sites
Pre - Synaptic terminals
Receptors
» Nicotinic agonists and antagonists
Autonomic Ganglia
» Muscarinic agonists and antagonists
Parasympathetic Effectors
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Adrenergic transmission sites
Pre - Synaptic terminals
» Release and synthesis of catecholamines
Receptors
» 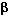 and
and 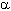 Adrenergic agonists and antagonists
Adrenergic agonists and antagonists
Inhibitors of catecholamine re-uptake and destruction
Histaminergic receptors & antagonists
Selected other stories
..
Presynaptic or axonal agents:
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) and Saxotoxin*
Batrachotoxin & scorpion toxin*
Botulinus toxin
Procaine (Novocain) & relatives
General anesthetics
Bind to voltage - gated Na+ channels and prevent them from opening
Inhibits axonal transmission of action potential
Procaine (Novocain), lidocaine, cocaine, benzocaine
Muscarinic agonists
(parasympathomimetic)
ACh*
Muscarine*
Amanita muscaria
Pilocarpine*
Pilocarpus
jaborandi
Furmethide
Muscarinic antagonists
Atropine*(belladonna)
Atropa belladonna, the deadly
nightshade
Datura stramonium, known as
Jamestown or jimsonweed, stinkweed,
thorn-apple, and devil's apple.
Scopalomine (hyoscine)
found chiefly in the shrub Hyoscyamus
niger (henbane) and
Scopolia carniolica.
Nicotinic agonists
ACh*
Nicotine*
DMPP
(1,1-dimethyl-4-phenylpiperazinium)
Nicotinic antagonists
Hexamethonium (C6)*
(at ANS ganglia)
Read the Hexamethonium Man on the Web site
d-Tubocurarine*
(CURARE)
Anti-Cholinesterases
Reversible & competitive:
Eserine*
Prostigmine
Irreversible & non-competitive:
Organophosphates
(DFPs)
-Tabun, Sarin, Soman
-Malathion & Parathion
Adrenergic 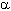 agonists
agonists
Epinephrine*
Norepinephrine*
Phenylephrine*
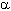 1 specific
1 specific
Psuedoephedrine (Sudafed)
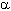 1 specific
1 specific
Phenylpropanolamine
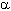 antagonists
antagonists
Phentolamine*
Phenoxybenzamine?*
Prazosin
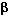 agonists
agonists
Epinephrine*
Isoproterenol*
Albuterol (Ventolin) 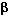 2
only
2
only
Norepinephrine (weak at 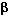 2)*
2)*
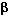 antagonists
antagonists
Propranolol*
Synthesis of NE
+ OH
phenylalanine --------> tyrosine
+ OH
tyrosine
--------> DOPA
- COOH
DOPA
--------> dopamine
+ OH
dopamine
--------> NE
EPI & NE Synthesis Inhibitors:
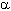 - methyl - p - tyrosine
- methyl - p - tyrosine
? - methyl DOPA (ALDOMET) - false
neurotransmitter
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
MAO breaks down catecholamines in adrenergic
nerve terminals
It is part of the regulatory mechanisms
that insure appropriate [NE] in nerve terminals
Inhibitors of NE Re-uptake
Anti - depressants
Amitriptyline
Desiprimine
Serotonin -
5 Hydroxytryptamine (5 HT)
Receptor is a transmembrane, G - linked
protein
Seven different receptor subtypes
LSD
CNS 5 HT agonist
PNS 5 HT antagonist
Inhibitors of Serotonin Re-uptake
Anti-depressants
Prozac
Zoloft
Paxil
Other adrenergic agents of
interest
(Meth)amphetamine
Reserpine
Histaminergic agents
Histamine*
Receptors
H1
H2
H3
Histamine
Relaxes vascular smooth muscle 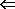 dilates blood vessels,
dilates blood vessels,
drops BP (large systemic response
that occurs during anaphylactic
shock) while usually increasing LOCAL
blood flow to site of localized
response (e.g., insect bite).
Contracts airway and intestinal smooth
muscles
Constricts airways - asthma
Contracts intestinal muscles - diarrhea
Increases capillary permeability - edema
Histaminergic Antagonists
Antagonists
- H1
Chlorpheniramine
Diphenhydramine
H2
cimetidine (TAGAMET), famotidine (PEPCID), nizatidine (AXID),
and ranitidine (ZANTAC)
Prostaglandin Synthesis Inhibitors
Acetyl salicylic acid - Aspirin
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Ibuprofen (Advil)
Naproxen (Aleve)
Indomethacin (Indocin)
Other Stuff
Endogenous Opioids
enkephalins, dynorphins, and ?- endorphins
Mu, kappa, and delta receptors
Exogenous Opioids
Morphine and heroin
Naloxone - opiate antagonist
Ethyl alcohol
Depresses neuron function
Vasodilation
Dont take a drink from the big dog!