Acid - Base Balance
HA <===> H+ + A-
Keq = [H+] + [A-]
[HA]
Henderson-Hasselbalch
Equation
[H+] = Keq x [HA]
[A-]
-log [H+] = -log Keq + log [A-]
[HA]
pH = pKa + log [A-]
[HA]
pKa
when pH = pK, acid is 50% dissociated
when pH = pK, 50% of buffer is in each form giving maximum buffering capacity
match pK of potential buffers to desired pH
Metabolism
Constant source of H+ and thus reduces plasma pH
Proteins --> H2SO4 , HCl, H3PO4
Fats --> ketone bodies such as acetone & b hydroxybutyric acid
Oxidation ---> H+ from CO2
Plasma Buffers
H2CO3
H3PO4 and organic phosphates
Proteins at ionized ‘R’ groups
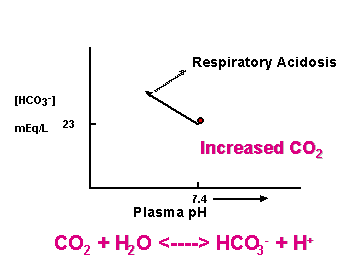
Plasma Bicarbonate
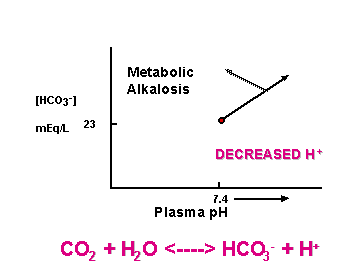
[HCO3-]plasma = 23 mEq/L
Changes indicate renal or respiratory problems
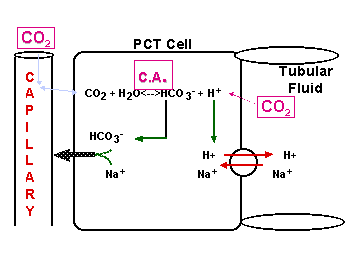
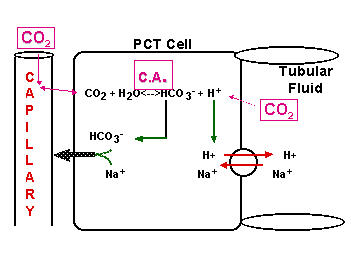
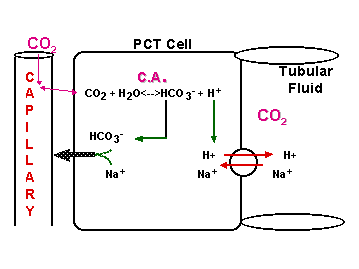
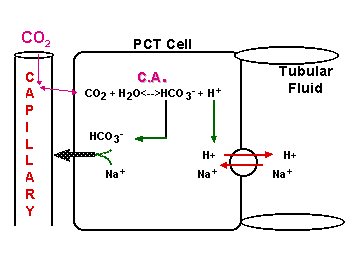
CO2 + H2O <----> HCO3- + H+
OPEN BUFFER SYSTEM!

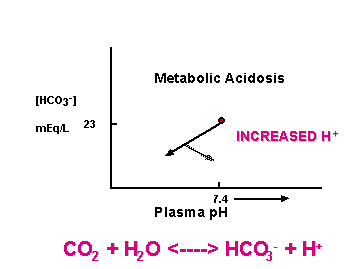
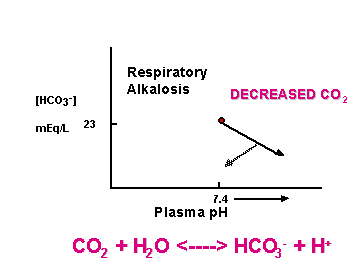
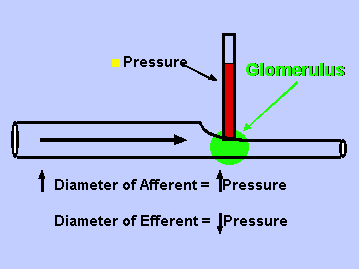
Some Clarifying Images?
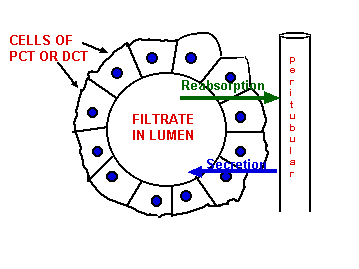
Cells of PCT & DCT