Gastrointestinal Physiology
Chapter 20
Salivary Glands
Parotid
amylase (ptyalin)
1 - 4 hexose linkages
Submaxillary & Sublingual
mucin (protein for lubrication)
Salivary Glands
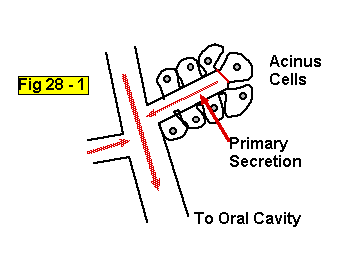
Acinus type glands:
Primary secretion by secretory cells and then modified by duct cells as saliva passes through on the way to the oral cavity
Saliva
As saliva flows down duct:
[Na+] and [Cl-] decrease
[HCO3-] and [K+] increase
p
also decreasesAs flow rates increase, this exchange is less complete


Salivary pH
Saliva pH is basic (vs. plasma pH)
WHY??
Consider Ca++ in teeth
Excitatory Signal Molecules
ACh from Parasympathetic NS onto muscarinic receptors
VIP from enteric NS
Increased blood flow in response to kininogen activation
Kininogen Activation
Glands release Kallikrein when activatedPlasma globulin
Results in peptide --> bradykinin
Bradykinin ---> local vasodilation (10X increase in BF)
Other Components of Saliva
Muramidase --> cleave muramic acid in bacterial cell walls
Lactoferrin --> binds Fe++
Epidermal growth factor --> stimulates mucosal cell growth
IgA
Lingual lipase (small amounts)
ABO antigens (secreters)
Regulation of Salivary Secretion
Cephalic Phase
Oral Phase
Gastric Phase
Vagal - vagal reflex
Enteric, Sympathetic, & Parasympathetic NS
Smooth Muscle & Structure of Gut
Stomach
Figures 20 - 1 through 4
Innervation of GI Tract
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
Enteric
local, intrinsic neurons
cell bodies in ganglia in GI walls
integration
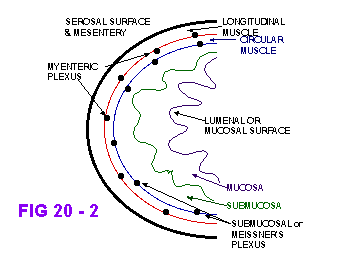
See Figs 20-2
Enteric Nervous System
Figs 20 - 2 & 19
Receptors
Mechano
Chemo
Thermo
Interneurons
Reflexes & ‘motor’ programs
Excitatory and Inhibitory motor neurons
Muscles
Blood vessels
Secretory cells
Enteric Nervous System
Vagus nerve contains afferent and efferent neurons to connect enteric n.s. with cns
Activity of enteric n.s. influenced by:
chemical composition
volume
Autonomic inputs
Sympathetic Actions
Inhibition:
decrease motility and secretion via
a2 and b2 receptorsdecreased blood flow via a1
decreased NT release by enteric system via 2 on presynaptic terminals
Parasympathetic
Excitation:
ACh on muscarinic receptors
directly onto muscle and secretory cells
directly onto enteric nerves to cause epsp’s
Smooth Muscle:
Chapter 12; pages 348 - 355
Small, discrete cells - 20 mm
Linked by gap junctions
Membrane invaginations - caveoli
Little SR
Actin & Myosin but no striations
Intermediate filaments
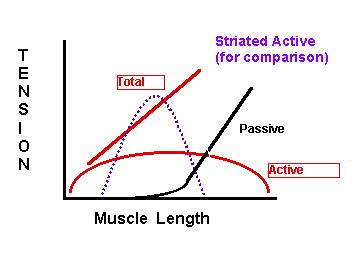
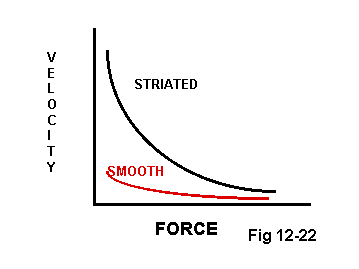
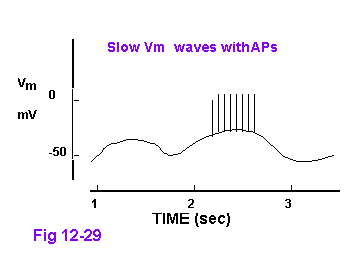
Smooth Muscle
Oscillating Vm
High GNa+ and variable GK+
Responds to stretch
Mysoin regulation of contraction

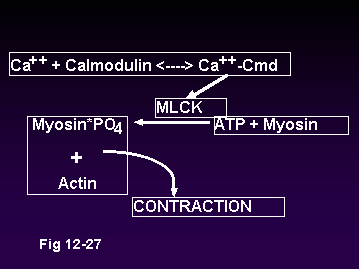
Ca++ for Contraction
Open membrane channels
Voltage gated membrane cannels
Ligand gated membrane channels
SR and ER
Released by IP3
Ca++ Removal
SR, ER, & Membrane Ca++ ATPase
Na+ - Ca++ exchange in membrane
STOMACH
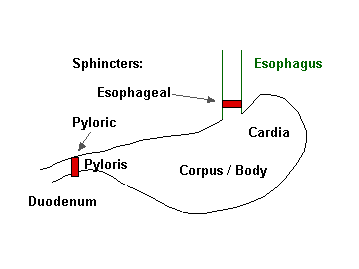
Stomach Mucosal Surface: Folds are called Rugae gastricae
Gastric Glands
Cardiac
mucus producing columnar cells
Pyloric
mucus and G cells producing peptide hormone gastrin
Oxyntic
Oxyntic Glands
Surface Epithelium - insoluble mucus
Neck Cells - soluble mucus
G cells - gastrin
Parietal (or oxyntic) Cells - HCl & Intrinsic Factor
Chief Cells - pepsinogen