MEASURING BLOOD VOLUME
6 - 8 % OF BODY WEIGHT IN Kg

PLASMA VOLUME
VOLUME = AMOUNT mg
CONCENTRATION mg / ml
USE A SUBSTANCE:
> 69,000 MW
NOT METABOLIZED
BLOOD VOLUME
CORRECT PLASMA VOLUME (PV) FOR HEMATOCRIT (HCT)
BLOOD VOL = P V x 1
1 - HCT
INTERSTITIAL FLUID VOLUME
VOL = AMT / CONC
USE INULIN
5,200 MW
NOT METABOLIZED
NOT TAKEN UP BY CELLS
TOTAL BODY WATER
USE D2O or 3H2O
ALLOW TIME FOR DISTRIBUTION AMONG COMPARTMENTS
USE USUAL EQUATION:
VOL = AMT / CONC
Calculating Renal BF:
Renal Measurements:
Renal Blood Flow
GFR
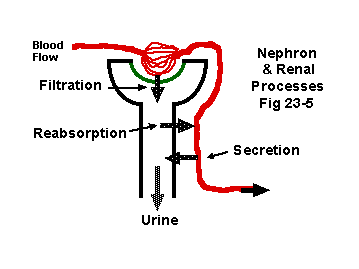
Renal processes
Filtration
Reabsorption
Secretion
To calculate Clearance & RBF,
Inject known amount of a solute, i.v.
Wait a few minutes
Measure PA in any artery
Measure PV in RENAL VEIN
Measure Rate of urine formation
Measure [solute]urine
Renal clearance
volume of plasma per minute needed to excrete the quantity of solute appearing in the urine in a minute
Renal Clearance:
The hypothetical volume of plasma from which a substance is completely removed per minute in one pass thorough the kidney
If there were 1 mg of Z in 100 ml of plasma, and
You found 0.5 mg of Z appearing in the urine/ min, then
the clearance of Z would = 50 ml of plasma
Clearance
C = U x V / PA
U = [solute] in urine (mg/ml)
V = volume of urine/min (ml/min)
PA = [solute] in arterial plasma (mg/100 ml plasma
Calculate Clearance
PA = 1.0 mg/100 ml plasma
U = 0.1 mg/ml
V = 1.0 ml/min
C = 0.1mg/ml x 1.0 ml/min
1.0 mg / 100 ml
C = 10 ml/min
Understanding Clearance:
If in this example, 0.1 mg of solute appears in urine / min, in how much plasma was that 0.1 mg delivered if PA = 1.0 mg/100 ml?
Answer = 10 ml/min
In other words, that 0.1 mg of solute that appeared in the urine/min was dissolved in 10 ml of plasma. Thus C = 10 mls/min.
Extraction Ratio (E)
The E of a solute is equal to the fraction of the substance that is removed from the plasma in one pass through the kidney:
E = PA - PV / PA
Calculate E
PA = 0.2 mg/100 ml
PV = 0.1 mg/100 ml
E = 0.2 - 0.1 / 0.2
E = 0.5
Renal Plasma Flow
RPF = C / E
RPF = 10 ml/min / 0.5
RPF = 20 ml / min
Renal Blood Flow
RBF = RPF x 1 / 1- hct
If hct = 0.5,
RBF = 20 ml/min x 1 / 1 - 0.5
RBF = 40 ml / min
Calculating Renal BF:
Substance PA PV U V
X 1.0 mg/100ml 0.8/100 0.2 mg/ml 1 ml/min
Y 1.0 0.3 0.7 1
Z 1.0 0.9 0.1 1
Hct = 0.50
To calculate RBF, first calculate C and E of substance with largest E
EY = 0.7
CY = 0.7 mg/ml x 1 ml/min
1.0 mg / 100 mls
CY = 70 ml / min
From C and E, calculate RPF:
RPF = C / E
RPF = 70 ml / min
0.7
RPF = 100 ml/ min
From RPF & Hct, calculate RBF:
RBF = RPF x 1
1 - Hct
RBF = 100 ml / min x 1
0.5
RBF = 200 ml / min
GFR = C of solute which is ONLY FILTERED, e.g., inulin.
WHY?
Inferences from GFR
If Csolute = GFR, solute is only filtered
If Csolute > GFR, solute is filtered and secreted
If Csolute < GFR, solute is filtered and reabsorbed
Filtration Fraction
FF = fraction of plasma that is made into filtrate
Usually = 0.2 in humans
Calculate:
FF = GFR / RPF
Inferences from FF:
If Esolute = FF, solute is only filtered
If Esolute > FF, solute is filtered and secreted
If Esolute < FF, solute is filtered and reabsorbed
Assume X from data set is only filtered
Then, GFR = CX = 0.2 x 1
1.0 / 100
GFR = 20 ml / min
FF = GFR / RPF
FF = 20 ml/min / 100 ml/min
FF = .2
Calculate Amount of a solute filtered / min:
Amount Filtered / min = PA x GFR
For Z, Amt Filt =
1.0mg/100 mls x 20 ml / min
Amt Filt = 0.2 mg / min
Amount of a Solute Appearing in Urine / min
Amt Urine = U x V
For Solute Z, Amt Urine =
0.1 mg / ml x 1 ml / min
Amt in Urine / min = 0.1 mg / min
Amount reabsorbed / min
= Amt filtered - Amt in Urine
= (GFR x PA) - (U x V)
= (20 ml/min x 1.0 / 100) -
(0.1 mg/ml x 1 ml/min)
= (0.2 mg/min) - (0.1 mg / min)
= 0.1 mg / min is reabsorbed
Amount Secreted / min
= Amt in Urine - Amt Filtered
= (U x V) - (PA x GFR)
= (0.7 mg/ml x 1 ml/min) -
(1.0 mg/ 100 ml x 20 ml/min)
= (0.7 mg/min) - (0.2 mg/min)
= 0.5 mg/min
Inferences:
If UV = GFR PA , solute is only filtered
If UV > GFR PA , solute is filtered and secreted
If UV < GFR PA , solute is filtered and reabsorbed