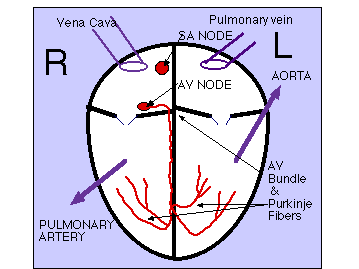
Review Heart Anatomy and Cardiac Muscle Cell Structure
CARDIAC CELL STRUCTURE

Blood Flow
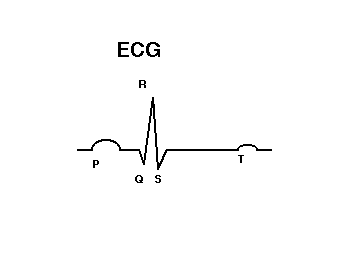
Electrical Activity of the Heart
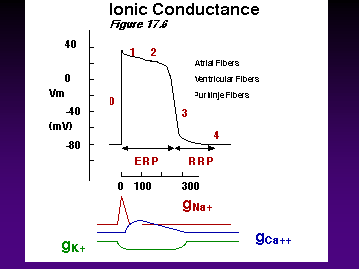
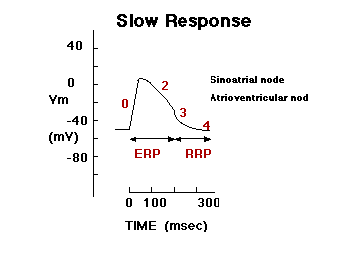
Note Differences in Conduction Velocity Due to Rates of Depolarization!
RECTIFICATION
Minimized efflux of K+ during AP plateau because of decreased K+ conductance at this positive Vm
TIME (in msec) <-50->
Ventricular action potential
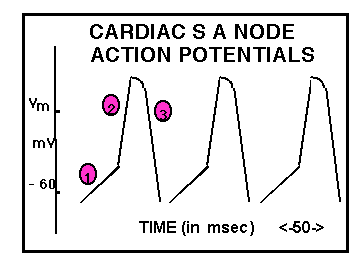
Terminology
Starling’s Law of the Heart:
AS VENTRICULAR FILLING (EDV) INCREASES, STROKE VOLUME and STRENGTH OF BEAT) ALSO INCREASES
OR
THE VENTRICLE PUMPS THE VOLUME THAT IT RECEIVES
STARLING’S LAW OF THE HEART
P = 2T/R
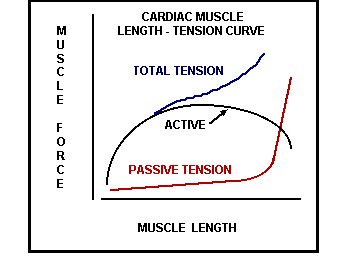
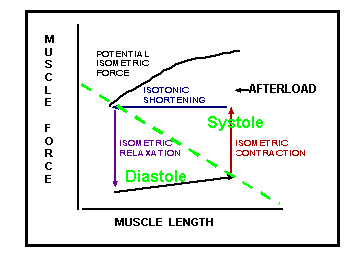
Starling’s Law of the Heart
Increased EDV or myocardial fiber length results in increased SV or increased strength of contraction.
Basis for Starling’s Law:
P = 2T/r
where
P = pressure in ventricle or aorta at ejection
T = myocardial tension required to generate that tension
r = radius of ventricle at beginning of systole
P = 2T/r
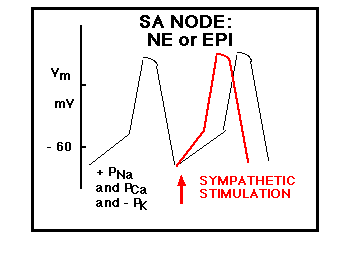
SYMPATHETIC RESPONSE
As heart rate increases,
filling time decreases
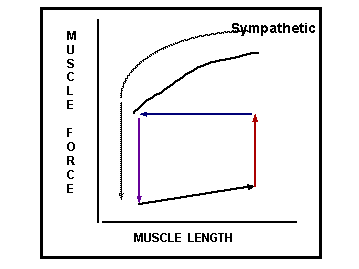
DIGITALIS:
DECREASE HR
BUT
INCREASE STRENGTH
POISEUILLE’S LAW
F = DPpr4
8 h L
F = DP / R
or
R = DP / F
P1 = 100 mm Hg P2 = 10 mm Hg
FLOW = 10 ml / min
R = DP / F
= 90 mm Hg / 10 ml/min
= 9 mm Hg / min/ml
= 9 PRU
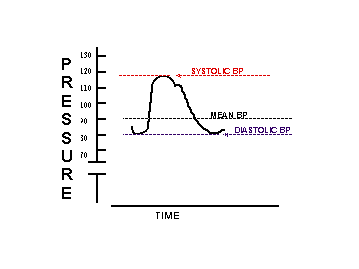
Blood Pressure
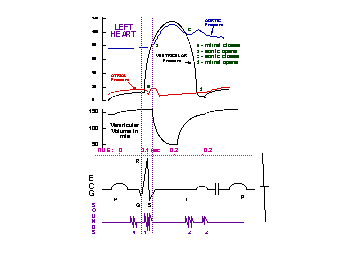
Sympathetic Response on Heart
B1 receptor activation
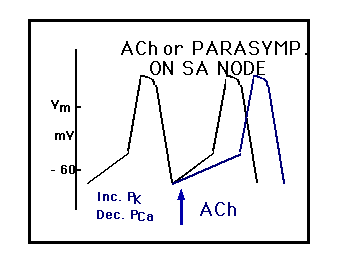
Vagus Nerve
PRESSURE MEASURED BY BARORECEPTORS
Why not measure blood flow (I.e., Cardiac Output)?
VAGUS NERVE